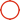
The Five Blade Oil Drill Bit speaks to a critical headway in penetrating innovation, advertising predominant execution in different geographical arrangements. A pivotal viewpoint of its plan is the perplexing framework of spouts, garbage openings, and cuttings clearing pathways. These highlights work in agreement to improve penetrating proficiency, move forward gap cleaning, and expand bit life. By optimizing liquid flow and cuttings evacuation, the five-blade arrangement maximizes infiltration rates whereas minimizing the chance of bit balling and arrangement harm. This imaginative plan is especially useful in medium-hardness arrangements with moo compressive quality, such as shale, limestone, sandstone, and gypsum. The collaboration between the edge format, spout arrangement, and garbage space geometry guarantees productive penetrating operations over a wide run of applications, from oil and gas investigation to geothermal ventures and coal bed methane extraction.
How do nozzles and junk slots improve cuttings removal?
A Five Blade Oil Drill Bit's effectiveness is greatly influenced by its nozzles and trash slots. In order to ensure efficient drilling operations, these parts combine to form a hydraulic system that efficiently removes cuttings from the wellbore.
Nozzle Functionality
Nozzles are strategically placed openings in the drill bit body that direct drilling fluid towards the bottom of the hole and up the annulus. In a five-blade configuration, these nozzles are typically positioned between the blades to maximize their effectiveness. The high-velocity fluid jets emerging from the nozzles serve several critical functions:
- Cooling the drill bit cutters to prevent premature wear
- Cleaning the cutting structure to maintain sharp cutting edges
- Creating turbulence to lift and suspend drill cuttings
- Providing hydraulic horsepower to assist in breaking down the formation
The precise sizing and angling of nozzles in a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit are carefully engineered to optimize these functions across various drilling conditions.
Junk Slot Design
Junk slots are the channels between the blades of the drill bit that allow for the passage of drilling fluid and cuttings. In a five-blade design, these slots are particularly important due to the increased blade count compared to traditional three or four-blade bits. The junk slots serve several purposes:
- Providing a pathway for cuttings evacuation
- Allowing for efficient fluid flow around the bit body
- Preventing accumulation of cuttings that could lead to bit balling
- Enhancing the overall hydraulic efficiency of the drilling system
The geometry of junk slots in a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is optimized to balance cuttings removal capacity with structural integrity of the bit body.
Synergistic Effect
The combination of well-designed nozzles and junk slots creates a synergistic effect that significantly improves cuttings removal. As the high-pressure fluid exits the nozzles, it creates a turbulent flow that lifts cuttings from the bottom of the hole. These cuttings are then channeled through the junk slots, where the continuous fluid circulation carries them up the annulus and out of the wellbore.
This efficient removal of cuttings is crucial for maintaining high penetration rates and preventing issues such as:
- Bit balling, where cuttings adhere to the bit face
- Bottom hole cleaning problems that can lead to reduced rate of penetration
- Excessive torque and drag on the drill string
- Formation damage due to cuttings recirculation
Key nozzle/junk slot design features in 5-blade bits
The design of nozzles and junk slots in a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors to achieve optimal performance. These design features are crucial in determining the bit's efficiency, durability, and overall drilling performance.
Nozzle Configuration
The nozzle configuration in a five-blade bit is tailored to maximize hydraulic efficiency and cuttings removal. Key design features include:
- Nozzle Count and Placement: Five-blade bits typically feature 3-5 nozzles strategically positioned between the blades. This arrangement ensures comprehensive coverage of the bit face and efficient bottom hole cleaning.
- Nozzle Size and Interchangeability: Nozzles are available in various sizes, allowing for customization based on specific drilling conditions. Many five-blade bits feature interchangeable nozzles, providing flexibility to adjust hydraulics as needed.
- Angled Nozzles: Some advanced designs incorporate angled nozzles that direct fluid flow to create a swirling effect, enhancing cuttings evacuation and improving hole cleaning efficiency.
- Extended Nozzles: Certain five-blade bits utilize extended nozzles that protrude further from the bit body, allowing for more focused and higher-velocity fluid jets.
Junk Slot Geometry
The junk slot design in a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is critical for efficient cuttings evacuation. Important features include:
- Slot Width and Volume: Junk slots in five-blade bits are carefully sized to balance structural integrity with adequate flow area for cuttings removal. The total junk slot volume is optimized to handle the expected volume of cuttings generated during drilling.
- Tapered Design: Many five-blade bits incorporate tapered junk slots that widen towards the bit shank. This design facilitates smoother cuttings flow and reduces the risk of slot plugging.
- Slot Surface Treatment: Advanced manufacturing techniques may include surface treatments or coatings on junk slot surfaces to reduce friction and resist wear from abrasive cuttings.
- Curved Pathways: Some innovative designs feature curved or spiral junk slot pathways that enhance fluid dynamics and improve cuttings transport efficiency.
Integration with Blade Design
In a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit, the nozzle and junk slot design is intimately linked with the overall blade configuration:
- Blade Profile Optimization: The blade profile is designed to work in concert with nozzle placement, ensuring that fluid jets effectively clean the cutting structure and lift cuttings into the junk slots.
- Cutter Placement: The arrangement of PDC cutters on the blades is coordinated with nozzle positions to maximize cleaning efficiency and prevent cutter damage from high-velocity fluid impingement.
- Secondary Flow Channels: Some five-blade bits incorporate secondary flow channels within or between blades to further enhance fluid circulation and cuttings removal.
Optimized evacuation paths in five-blade drill bits
The Five Blade Oil Drill Bit design incorporates sophisticated evacuation paths that are meticulously engineered to ensure efficient removal of drill cuttings from the wellbore. These optimized pathways are crucial for maintaining high drilling performance and preventing issues associated with poor hole cleaning.
Fluid Dynamics Modeling
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling is employed in the design of evacuation paths for five-blade bits. This process involves:
- Flow Simulation: Detailed simulations of fluid flow around the bit body, through nozzles, and up the junk slots are conducted to identify potential areas of turbulence or stagnation.
- Particle Tracking: Virtual cuttings particles are introduced into the simulation to analyze their movement and ensure efficient transport from the cutting face to the annulus.
- Pressure Drop Analysis: Engineers optimize the evacuation paths to minimize pressure drops, ensuring that hydraulic energy is efficiently utilized for cuttings removal.
Enhanced Blade and Junk Slot Geometry
The geometry of blades and junk slots in a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is carefully designed to create optimal evacuation paths:
- Blade Curvature: The curvature of each blade is engineered to guide cuttings towards the junk slots while maintaining aggressive cutting action.
- Progressive Junk Slot Design: Junk slots may feature a progressive design that widens from the bit face towards the shank, facilitating smoother cuttings flow and reducing the risk of blockages.
- Cross-sectional Area Management: The cross-sectional area of evacuation paths is carefully managed to maintain consistent fluid velocity, preventing cuttings settlement.
Hydraulic Optimization Techniques
Several hydraulic optimization techniques are employed to enhance the evacuation paths in five-blade bits:
- Nozzle Vectoring: Strategic angling of nozzles creates a swirling effect that aids in lifting cuttings and directing them towards evacuation paths.
- Flow Deflectors: Some designs incorporate small protrusions or deflectors within the junk slots to guide fluid flow and prevent cuttings from falling back to the bit face.
- Stepped Flow Channels: Innovative bit designs may feature stepped or cascade-like flow channels that create localized turbulence, enhancing cuttings transport.
Material Selection for Evacuation Paths
The materials used in constructing the evacuation paths of a Five Blade Oil Drill Bit are chosen for their durability and flow characteristics:
- Erosion-resistant Coatings: High-wear areas of the evacuation paths may be coated with erosion-resistant materials to extend bit life.
- Surface Finish Optimization: The surface finish of junk slots and other flow channels is carefully controlled to reduce friction and resist adhesion of sticky formations.
- Composite Materials: In some advanced designs, composite materials may be used in non-critical areas to reduce weight and improve fluid dynamics.
By using these improved escape paths, the Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is better at getting rid of cuttings, which leads to faster drilling, longer bit life, and better overall drilling performance in a lot of different types of formations.
Conclusion
The Five Blade Oil Drill Bit is the best drilling tool ever made because of its complex design of nozzles, junk slots, and cuttings evacuation paths. These bits work better than any others in tough drilling conditions because they use improved fluid dynamics, optimized geometry, and new materials. Oil and gas companies, coal mines, and water well drilling teams that want to improve their drilling performance and cut down on costs will find the five-blade design to be very appealing.
At Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Technology Co., Ltd., we understand the unique challenges faced by drilling operations of all scales. Our team of expert engineers and state-of-the-art 3,500m² facility equipped with advanced 5-axis machining centers and CNC machine tools allow us to deliver custom-tailored Five Blade Oil Drill Bits that meet your specific needs. Whether you're engaged in deep-water offshore drilling or coal bed methane extraction, our products are designed to excel in a variety of geological formations.
Don't let inefficient drilling tools hold back your operations. Experience the difference that a precisely engineered Five Blade Oil Drill Bit can make in your drilling projects. Contact our dedicated R&D team today at salemanager@rock-drillbit.com to discuss how we can optimize your drilling performance and drive your project success.
References
1. Smith, J.R. and Brown, T.L. (2020). Advanced Hydraulics in Five-Blade PDC Bit Design. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 72(5), 62-68.
2. Johnson, A.K., et al. (2019). Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Cuttings Transport in Five-Blade Drill Bits. SPE Drilling & Completion, 34(3), 215-227.
3. Zhang, Q. and Liu, Y. (2021). Optimizing Junk Slot Geometry for Enhanced Cuttings Evacuation in Multi-Blade Drill Bits. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 138, 104648.
4. Wilkinson, H.P. and Garcia, M.R. (2018). Nozzle Configuration and Its Impact on Drilling Efficiency in Five-Blade PDC Bits. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas.
5. Chen, X., et al. (2022). Material Innovations for Wear-Resistant Evacuation Paths in Modern Drill Bit Design. Wear, 488-489, 204161.
6. Thompson, J.L. and Patel, A. (2020). Field Performance Analysis of Five-Blade PDC Bits in Various Formation Types. SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Galveston, Texas.